Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
北村 智; 大野 豊; 鳴海 一成*
no journal, ,
今までほとんど分かっていなかった、シロイヌナズナにおけるアントシアニン蓄積機構を解明するために、banyuls変異体にイオンビームを再照射し、種子の赤色色素蓄積が低下した変異体pab1を得た。分子生物学的解析から、pab1の原因遺伝子は、シロイヌナズナ種皮のアントシアニン蓄積を支配する遺伝子であると考えられた。
中村 進一*; 鈴井 伸郎; 尹 永根; 石井 里美; 河地 有木; 頼 泰樹*; 服部 浩之*; 藤巻 秀
no journal, ,
Cadmium (Cd) is one of toxic heavy metals for us. Its accumulation in crop plants causes serious health problems. Elucidation of mechanisms of Cd behaviors in plants is needed in order to reduce Cd accumulation in crop plants. In our previous work, we confirmed that glutathione (GSH), applied to roots site specifically, inhibited Cd transport from roots to shoots in oilseed rape plants. In this work, we investigated effects of GSH, applied to roots, on Cd efflux from roots in oilseed rape plants. Cd efflux from roots in these plants were also visualized and analyzed by using PETIS (Position Emitting Tracer Imaging System). Oilseed rape plants used in experiments were grown hydroponically in a green chamber under controlled growth conditions. After each treatment, Cd efflux from roots in tested plants was evaluated using an atomic absorption spectrometer. There were different effects of Cd efflux from roots on glutathione, reduced form (GSH) and oxidized form (GSSG). PETIS experiments also indicated that GSH and GSSG, applied to roots, have different effects on Cd efflux from roots.
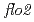 mutant of Arabidopsis using
mutant of Arabidopsis using  CO
CO and a positron-emitting tracer imaging system (PETIS)
and a positron-emitting tracer imaging system (PETIS)石井 陽平*; 鈴井 伸郎; 尹 永根; 河地 有木; 石井 里美; 栗田 圭輔; 島田 浩章*; 藤巻 秀
no journal, ,
The gene 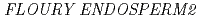 (
(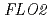 ) is widely distributed in plants. The
) is widely distributed in plants. The 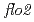 mutant of rice is known to have decreased expression of genes involved in production of storage starch. In this study, we analyzed the phenotype of
mutant of rice is known to have decreased expression of genes involved in production of storage starch. In this study, we analyzed the phenotype of 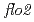 mutation in Arabidopsis from the aspect of carbon movement. 20 individuals each of
mutation in Arabidopsis from the aspect of carbon movement. 20 individuals each of 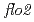 and WT (Col-0) were grown for 21 days. Starch accumulation in the whole plant of
and WT (Col-0) were grown for 21 days. Starch accumulation in the whole plant of 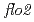 mutants was lower than WT. In contrast, the leaf areas and the fresh weights of
mutants was lower than WT. In contrast, the leaf areas and the fresh weights of 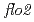 were larger and heavier than those of WT. We evaluated activity of carbon assimilation and source-to-sink translocation in
were larger and heavier than those of WT. We evaluated activity of carbon assimilation and source-to-sink translocation in 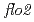 and WT using
and WT using  CO
CO tracer gas and PETIS, a noninvasive imaging system of radiotracers. As a result, the activity of carbon assimilation per leaf weight did not show difference between
tracer gas and PETIS, a noninvasive imaging system of radiotracers. As a result, the activity of carbon assimilation per leaf weight did not show difference between 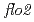 and WT; however, the carbon translocation rate from the leaves to sink tissues was lower in
and WT; however, the carbon translocation rate from the leaves to sink tissues was lower in 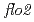 than in WT. These results imply the following mechanisms. Biosynthesis of starch in both of the source and sink tissues is decreased by
than in WT. These results imply the following mechanisms. Biosynthesis of starch in both of the source and sink tissues is decreased by 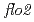 mutation. Sucrose accumulation in the sink tissue reduces the source-to-sink translocation. Excess sucrose in the source tissue causes the leaf expansion.
mutation. Sucrose accumulation in the sink tissue reduces the source-to-sink translocation. Excess sucrose in the source tissue causes the leaf expansion.